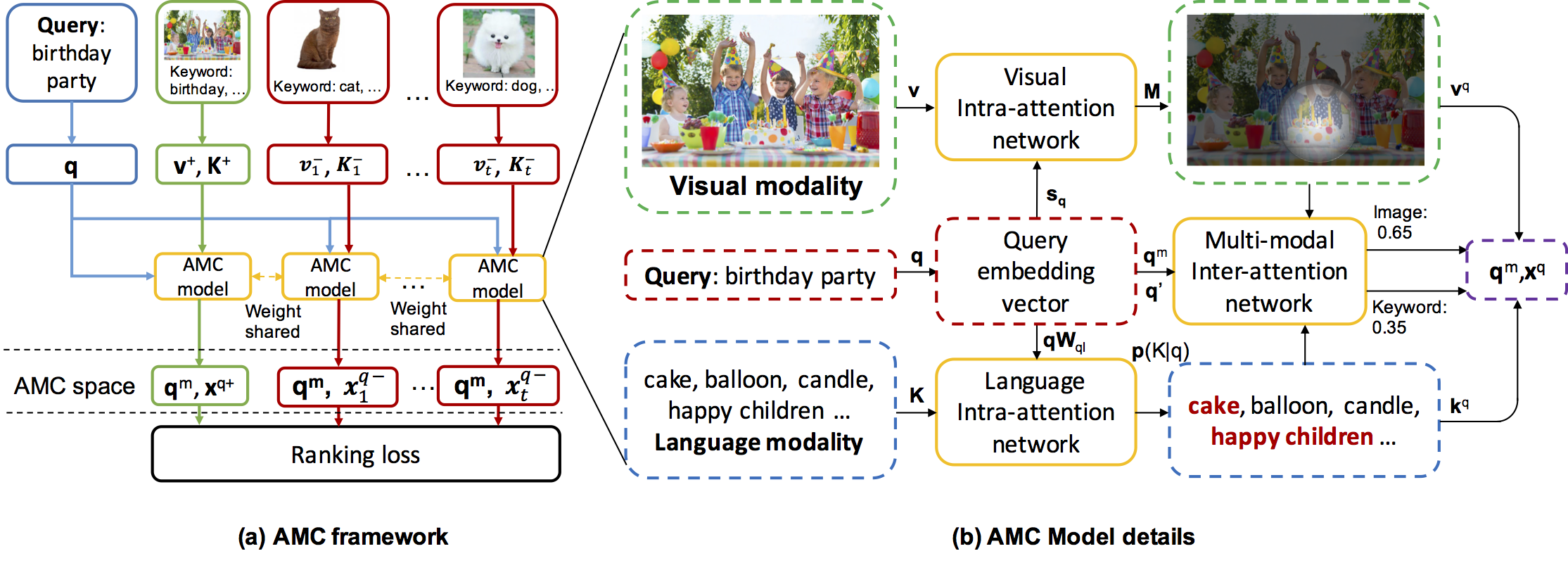
Attention guided Multi-modal Correlation Learning for Image Search
We leverage visual and textual modalities for image search by learning their correlation with input query. According to the intent of query, attention mechanism can be introduced to adaptively balance the importance of different modalities. We propose a novel Attention guided Multi-modal Correlation (AMC) learning method which consists of a jointly learned hierarchy of intra and inter-attention networks.
View Details Github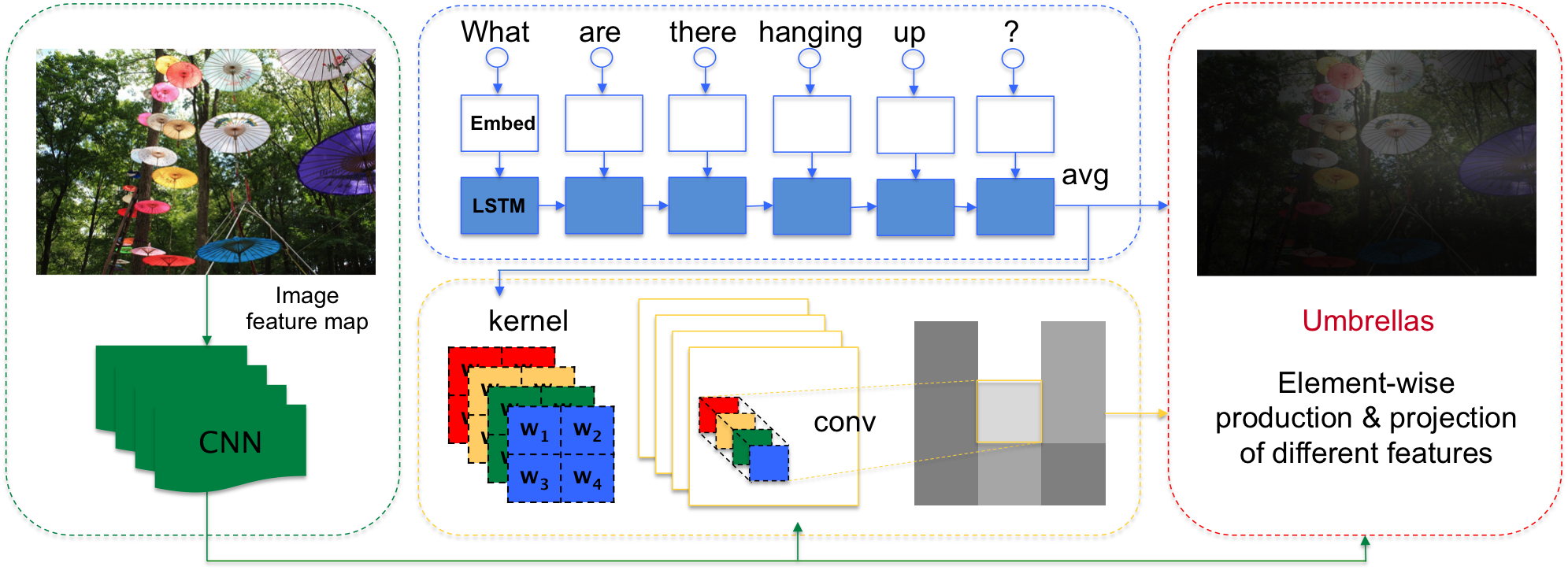
Attention Based Model in Visual Question Answering
Visual question answering task (VQA) automatically generates an answer for a given image and an image-related question. Attention is of significant importance in VQA because different questions inquire about different image regions. We propose an attention model for VQA that explicitly exploits the questions to guide the attention to generate appropriate answers.
View Details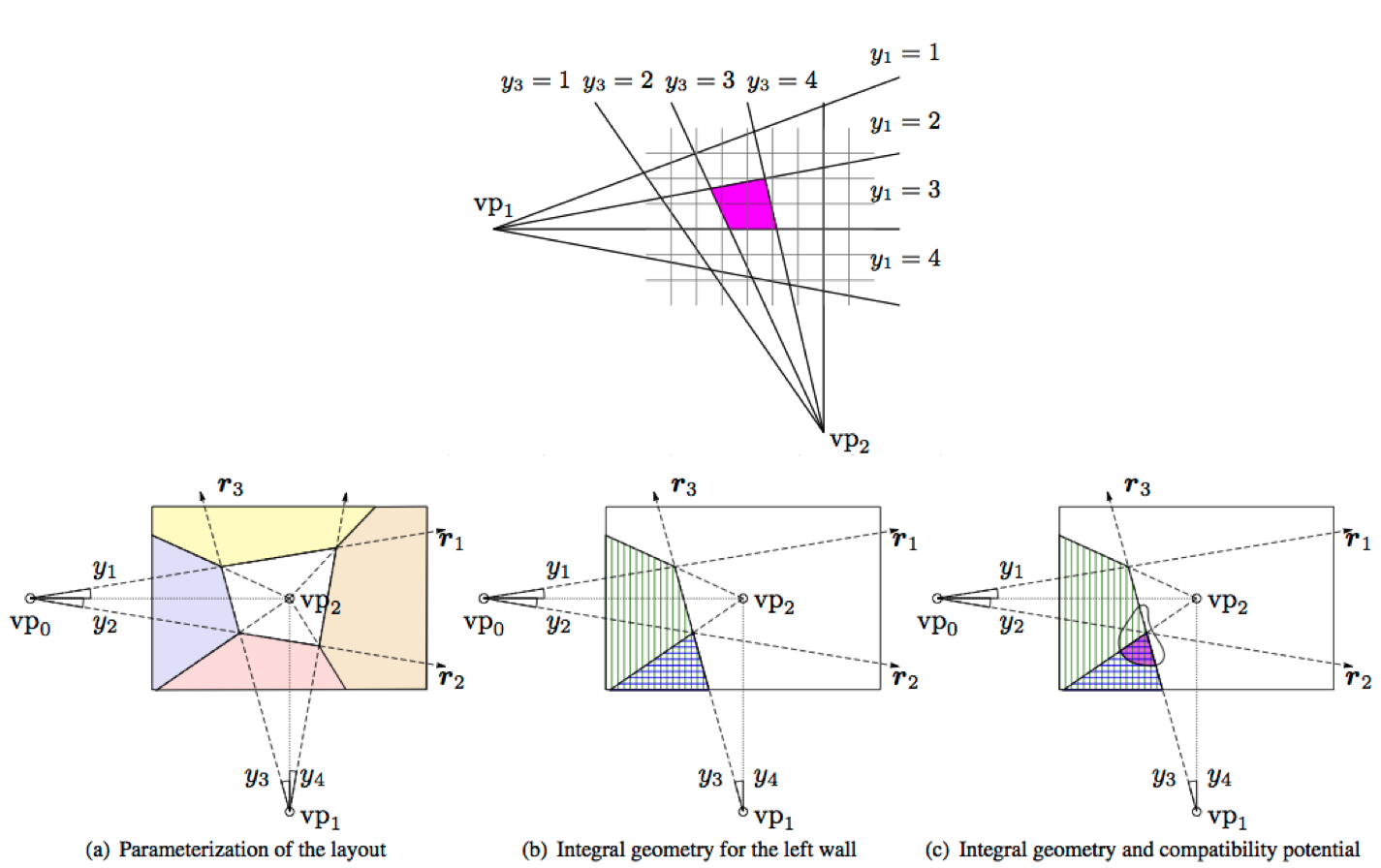
Estimating the 3D Layout of Indoor Scenes and its Clutter from Depth Sensors
In this paper we propose an approach to jointly estimate the layout of rooms as well as the clutter present in the scene using RGB-D data. Towards this goal, we propose an effective model that is able to exploit both depth and appearance features, which are complementary. Furthermore, our approach is efficient as we exploit the inherent decomposition of additive potentials. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on the challenging NYU v2 dataset and show that employing depth reduces the layout error by 6% and the clutter estimation by 13%.
View Details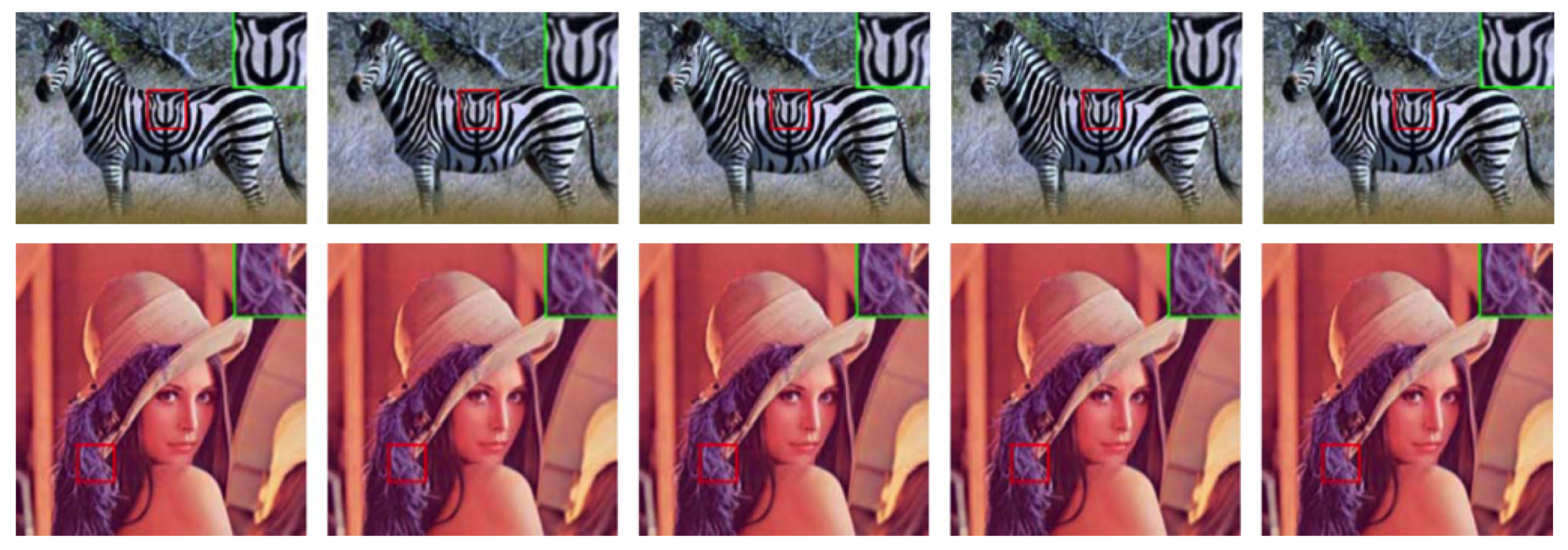
Image Super-Resolution Via Analysis Sparse Prior
In this letter, we present a new algorithm for a single image super-resolution using the analysis sparse prior in the l-alpha-beta color space. Experimental results show that our algorithm outperforms other existing state-of-the-art methods. In addition, due to the high scalability of our algorithm, key modules of the proposed algorithm can be integrated with other super resolution algorithms.
View Details